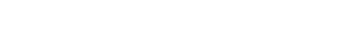
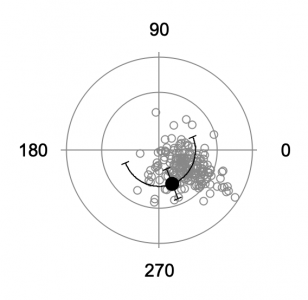
Polar averaging and errors
Averaging waves with polar data (list of angles) will give incorrect results in many cases (see image below). This function does a vector summation of X and Y components to determine the average angle, the standard deviation, or the standard error.
Function polarAvgErr(inWave,opStr,degrad) Wave inWave //single wave with list of angles //opStr = "avg", "sdev", or "sem" //degrad = "deg" or "rad" depending on the input data type String opStr,degrad Variable i,size,avgX,avgY,avg,sdev,sem,errX,errY,value,multiplier size = DimSize(inWave,0) Make/FREE/N=(size) xTotal,yTotal //input is degrees or radians strswitch(degrad) case "deg": xTotal = cos(inWave * pi/180) yTotal = sin(inWave * pi/180) multiplier = 180/pi break case "rad": xTotal = cos(inWave) yTotal = sin(inWave) multiplier = 1 break endswitch //polar average avgX = mean(xTotal) avgY = mean(yTotal) avg = atan2(avgY,avgX)*multiplier If(avg < 0) avg += 360 EndIf //polar standard deviation For(i=0;i<size;i+=1) errX += (xTotal[i] - avgX)^2/(size-1) errY += (yTotal[i] - avgY)^2/(size-1) EndFor errX = sqrt(errX) errY = sqrt(errY) sdev = atan2(errY,errX)*multiplier //polar standard error of the mean sem = sdev/sqrt(size) //select return parameter strswitch(opStr) case "avg": value = avg break case "sdev": value = sdev break case "sem": value = sem break endswitch return value End

Forum

Support
Gallery
Igor Pro 10
Learn More
Igor XOP Toolkit
Learn More
Igor NIDAQ Tools MX
Learn More

You may want to look at StatsCircularMoments as it may save you some coding.
December 5, 2018 at 12:20 pm - Permalink
In reply to You may want to look at… by Igor
ahh, thank you - there's always a new function to discover...
December 5, 2018 at 12:24 pm - Permalink
I find the description and polar plots a little confusing. You imply that the only input is a 1-D wave of polar angles (or you use only the angular part of a {theta, r} wave), but the data set has multiple 'r' values. Are you selecting a constant-r set of values from your presented data?
Another approach for full 2-D (x,y) or (r,theta)-->(x,y) data might be to first perform a linear ODR fit to an (x,y) line constrained to pass through the origin to find the best-fit average angle. Then find the difference angle for each point to get the set of d_theta's for the standard deviation calculation. I note that StatsCircularMoments seems to apply only to 1-D data at a fixed radius.
December 6, 2018 at 08:25 am - Permalink